最近,我看到了一张截图,展示了两个 Cypress 测试,它们使用了强大的 cy.intercept 命令来测试加载消息和错误处理。你可以在 Twitter 和 LinkedIn 上看到原帖。以下是截图内容:
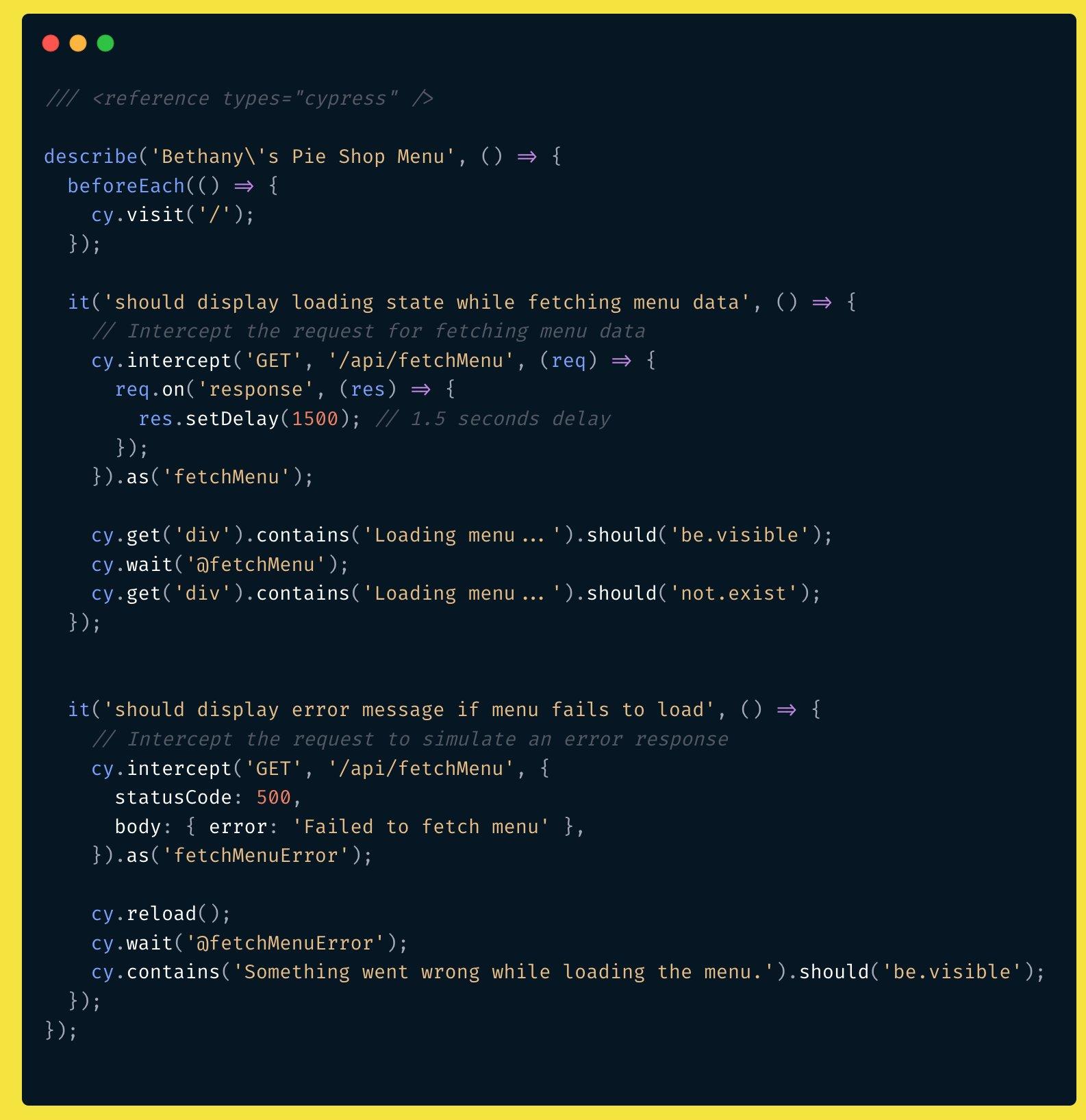
两个使用 cy.intercept 命令的 Cypress 测试
让我们稍微改进一下这些测试。
在执行动作之前设置网络拦截
我们要做的第一个改进是消除第一个测试中的潜在不稳定因素:
// cypress/e2e/bonus134.cy.js
describe('Page loads slowly', () => {
beforeEach(() => {
cy.visit('/loading.html')
})
it('shows the loading element', () => {
cy.intercept('GET', '/fruit', (req) => {
req.on('response', (res) => {
res.setDelay(1500) // 1.5 seconds delay
})
}).as('fetchFruit')
cy.get('div').contains('loading').should('be.visible')
cy.wait('@fetchFruit')
cy.get('div').contains('loading').should('not.exist')
})
该测试可能会通过,但存在一个问题。

第一个测试通过了
你看到了这个测试中的潜在问题吗?如果没有,请阅读博客文章《Cypress cy.intercept 问题》中的“拦截器注册得太晚了”部分。如果我们修改应用代码并让加载调用更早开始执行,就能看到错误。

如果网络调用发生的很快,第一个测试会失败
我们应该始终在应用程序进行调用之前注册网络拦截器。我将 cy.visit 移动到测试中,并将其放在 cy.intercept 命令之后。
it('shows the loading element', () => {
cy.intercept('GET', '/fruit', (req) => {
req.on('response', (res) => {
res.setDelay(1500) // 1.5 seconds delay
})
}).as('fetchFruit')
// once the network intercept is set up
// visit the page which kicks off the request
cy.visit('/loading.html')
cy.get('div').contains('loading').should('be.visible')
cy.wait('@fetchFruit')
cy.get('div').contains('loading').should('not.exist')
})
上面的测试更加健壮,应该始终能正常工作。
检查加载元素
我注意到很多人使用 cy.get(selector).contains(text) 命令。cy.contains 命令已经支持 cy.contains(selector, text) 参数,大多数情况下不需要将它与 cy.get 链接。上面的测试可以重写为:
it('shows the loading element (2)', () => {
cy.intercept('GET', '/fruit', (req) => {
req.on('response', (res) => {
res.setDelay(1500) // 1.5 seconds delay
})
}).as('fetchFruit')
cy.visit('/loading.html')
cy.contains('#fruit', 'loading').should('be.visible')
cy.wait('@fetchFruit')
cy.get('#fruit').should('not.contain', 'loading')
})
提示:我们可以通过检查 #fruit 元素是否显示了服务器返回的水果信息来使测试更加强大。
延迟响应
在我们的测试中,我们只是监视网络调用。调用仍会发送到服务器并返回真实数据,我们只是将响应发送到浏览器的时间延迟了 1.5 秒。可以将其简化为:
it('shows the loading element (3)', () => {
cy.intercept('GET', '/fruit', () =>
Cypress.Promise.delay(1500),
).as('fetchFruit')
cy.visit('/loading.html')
cy.contains('#fruit', 'loading').should('be.visible')
cy.wait('@fetchFruit')
cy.get('#fruit').should('not.contain', 'loading')
})
我们将请求发送到服务器的时间延迟了 1.5 秒,这与我们测试中的延迟相同。
第二个测试
原始截图中的第二个测试验证了一个错误场景。我们对网络调用进行了模拟,返回了状态码 500。提示:在模拟网络调用时,我们可以立即设置响应延迟。
beforeEach(() => {
cy.visit('/loading.html')
})
it('should display error message', () => {
cy.intercept('GET', '/fruit', {
statusCode: 500,
}).as('fetchFruit')
cy.wait('@fetchFruit')
cy.contains('HTTP error 500')
})
// after
it('should display error message', () => {
cy.intercept('GET', '/fruit', {
statusCode: 500,
}).as('fetchFruit')
cy.visit('/loading.html')
cy.wait('@fetchFruit')
cy.contains('HTTP error 500')
})
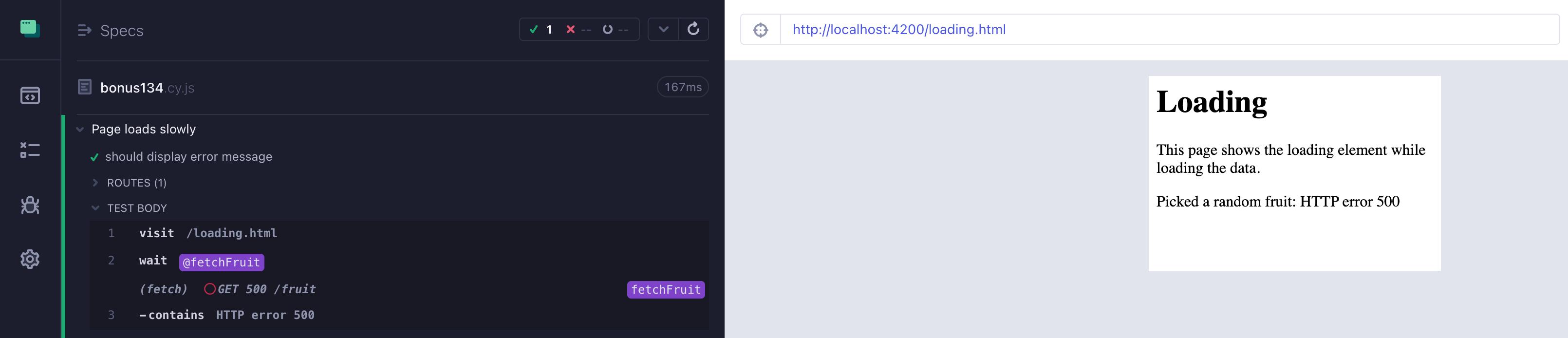
测试应用程序的网络错误处理
提示:在使用 cy.intercept 模拟网络调用时,可以很轻松地使用内置的响应存根对象属性 delay 来延迟响应。
it('should display error message after a delay', () => {
cy.intercept('GET', '/fruit', {
statusCode: 500,
delay: 1500,
}).as('fetchFruit')
cy.visit('/loading.html')
cy.contains('#fruit', 'loading').should('be.visible')
cy.wait('@fetchFruit')
// the error message should be displayed really quickly
cy.contains('#fruit', 'HTTP error 500', {
timeout: 0,
}).should('be.visible')
})
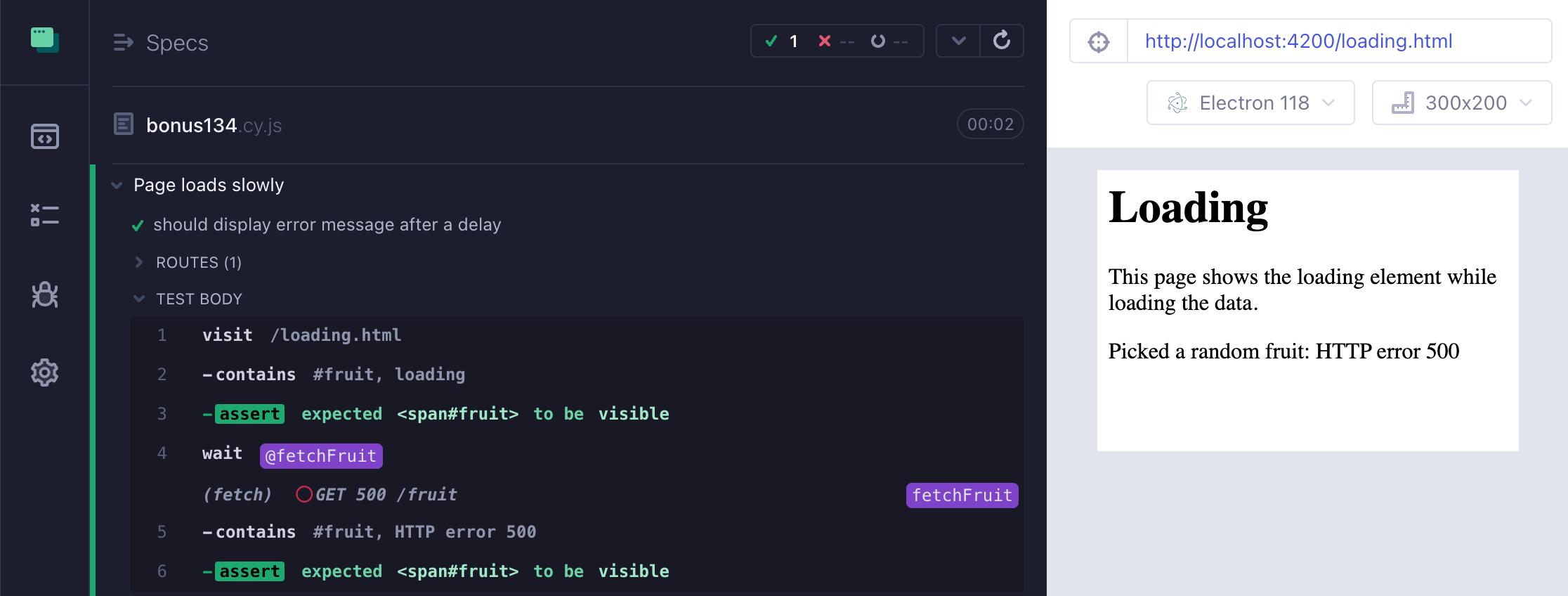
测试应用程序的加载状态和错误处理
